
Dr. Karen Hecht & Carl Pradelli Discuss Astaxanthin
In this episode of the NatureCity Podcast, Dr. Karen Hecht discusses astaxanthin, Nature's most potent secret. Astaxanthin is a form of phytoalexi...
Continue Reading
In this episode of the NatureCity Podcast, Dr. Karen Hecht discusses astaxanthin, Nature's most potent secret. Astaxanthin is a form of phytoalexi...
Continue Reading
Welcome to another fascinating episode of the NatureCity Podcast! In this special installment, Carl is joined by Andrea Zangara, the Director of S...
Continue Reading
Today, we explore the world of cherries for use in supplements – and more specifically the unique benefits of tart cherries. These cherries offer...
Continue Reading
In this episode, Carl continues to address your questions on how to protect you and loved ones from fake supplements, focusing on the importance o...
Continue Reading
In this week’s episode, we delve into the concerning issue of fraudulent products in the supplement marketplace. Reports are finding this problem ...
Continue Reading
Welcome back to another episode of the NatureCity Podcast, where we bring you the latest insights on natural supplement ingredients and how they c...
Continue Reading
David Foreman is known as the “Herbal Pharmacist due to his extensive knowledge about the plant world and how it can help us live better and age b...
Continue Reading
In this episode of the NatureCity Podcast, Host and Co-Founder of NatureCity Carl Pradelli, discusses lutein, a powerful antioxidant essential to ...
Continue Reading
Carl sits down with Jodi-Ann Blackwood from Bionap USA, to discuss the unique Morosil extract from Italy that was recently named “Ingredient of th...
Continue Reading
In this episode, our host, Carl Pradelli, sits down with resveratrol expert Marcia da Silva Pinto, to discuss the fascinating topic of resveratrol...
Continue Reading
In this episode, Carl Pradelli, the CEO and co-founder of NatureCity, the health benefits of resveratrol and why you should make it part of your d...
Continue Reading
This week’s episode is all about GABA, a powerful neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in helping us stay focused, concentrate, and maintai...
Continue Reading
As we age, maintaining our mental sharpness becomes increasingly important, and this is a concern shared by both older adults and younger individu...
Continue Reading
This episode of the 'NatureCity Podcast', hosted by Carl Pradelli, CEO and co-founder of NatureCity, focuses on the TrueProstate product - a supp...
Continue Reading
In this episode, NatureCity host Carl Pradelli sits down with Dr. Christopher Bailey, the Director of Scientific Affairs at Gencor. Dr. Bailey bre...
Continue Reading
This week, we’re discussing the benefits of organic plant calcium as a supplement for bone density – and why it’s better than the calcium found in...
Continue Reading
Carl shares why the price of many fish oil supplements has been skyrocketing (and may be headed higher) and some products are no longer available...
Continue Reading
In today's episode, we dive into the groundbreaking way to get more omega-3s from your fish oil supplement into your bloodstream with the novel Aq...
Continue Reading
In this episode, Carl dives deep into the world of omega-3s and their impact on heart health. He discusses a study from Denmark involving 54,000 a...
Continue Reading
In this episode, Carl dives deep into the world of omega-3s and their impact on heart health. He discusses a study from Denmark involving 54,000...
Continue Reading
In this week’s episode of the NatureCity Podcast, Carl shares his personal experience with oral probiotics for the mouth and throat areas. If you’...
Continue Reading
In this episode of NatureCity, Carl Pradelli discusses how to enhance energy and improve workout performance without relying on stimulants. Carl s...
Continue Reading
Welcome to this week's episode of the NatureCity podcast! In this episode, we discuss how to best supplement with magnesium, one of the most impo...
Continue Reading
In this episode, we dive into the importance of probiotics and prebiotics for gut and digestive health and how they impact overall health. We dis...
Continue Reading
In this episode, we dive into the importance of probiotics and prebiotics for gut and digestive health and how they impact overall health. We dis...
Continue Reading
In this episode of the NatureCity Podcast, Host and Founder of NatureCity Carl Pradelli, explores how Vitamin K2 and D3 work together to help you ...
Continue Reading
This episode is part 2 in the 2-part series where Carl breaks down the exciting new research with the revolutionary TamaFlex joint health ingredien...
Continue Reading
This is the 3rd published research study demonstrating the many ways TamaFlex can help your joints – and improve daily movement and function. The n...
Continue Reading
In this episode of The NatureCity Podcast, we're talking to Eric Anderson about his powerful new joint health innovation Tamaflex, which is a un...
Continue Reading
In this episode, Carl reviews the role of keratin in hair, skin and nail health, and discusses the form you should look for in supplements, whic...
Continue Reading
Carl delves into the topic of blood sugar swings and their impact on weight management. With a focus on understanding the effects of carbohydrates...
Continue Reading
In this episode of the NatureCity Podcast, Host and CEO of NatureCity Carl Pradelli explores the benefits of Vitamin E and what you need to know if...
Continue Reading
In this week’s episode, Carl discusses Crominex 3+, our preferred choice for supplements and its superior function in helping to convert carbohyd...
Continue Reading
Welcome back to the Nature City podcast! In today's episode, we have an exciting topic to discuss: a better form of the Berberine plant extract th...
Continue Reading
Welcome back to the Nature City Podcast! In today's episode, Carl is joined by Jocelyn Berube as they dive into the important topic of metabolic ...
Continue Reading
Want to be happier? Then look at the health of your gut! The health of your gut affects your brain and how you feel and on this episode of the Nat...
Continue Reading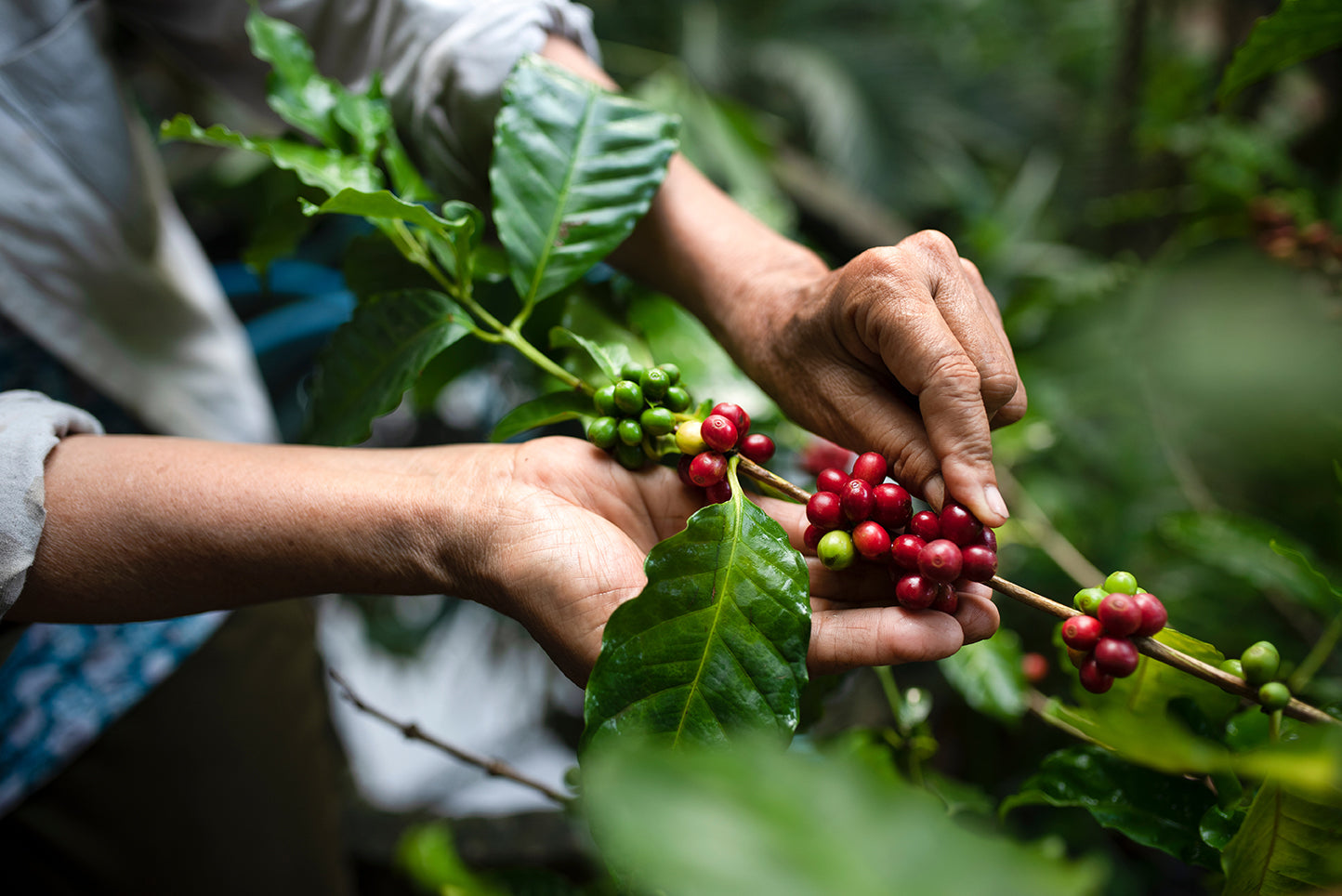
In this episode, Carl discusses the increasingly popular coffee berry fruit extract called NeuroFactor, which recently won “Ingredient of the Yea...
Continue Reading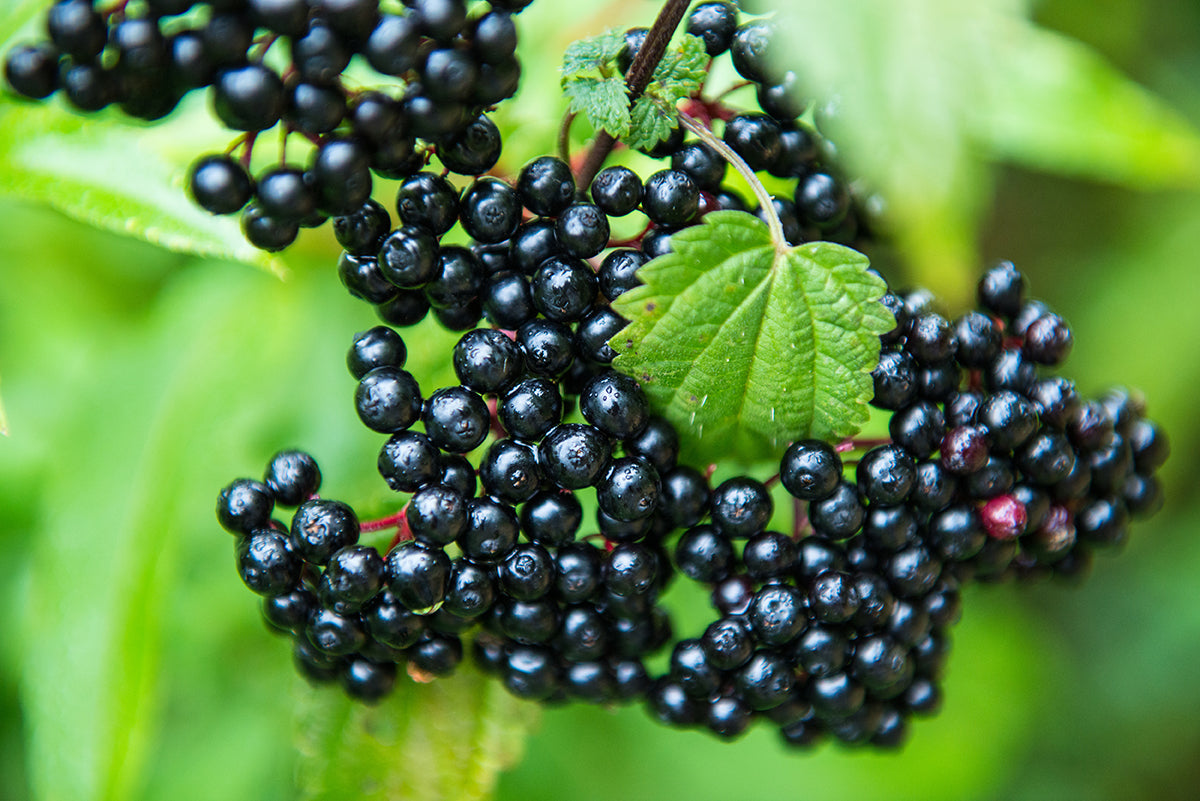
In today's episode, special guest, Erik Kenison from Nutriscience, joins us to discuss the novel ElderMune elderberry ingredient for supplements. ...
Continue Reading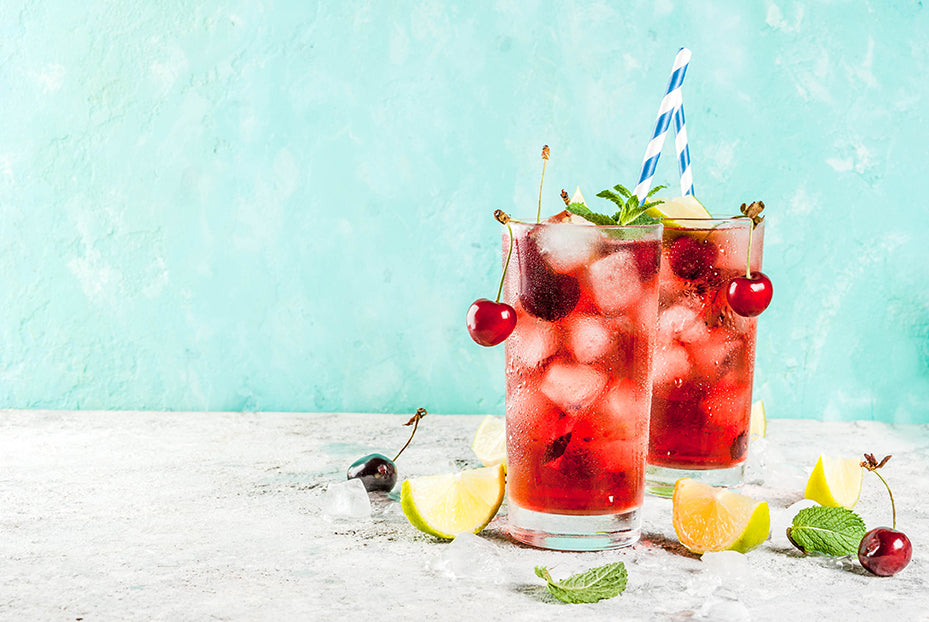
Many fruit and vegetable blends contain a long list of impressive sounding ingredients, but what can they actually do for you? In this episode, Car...
Continue Reading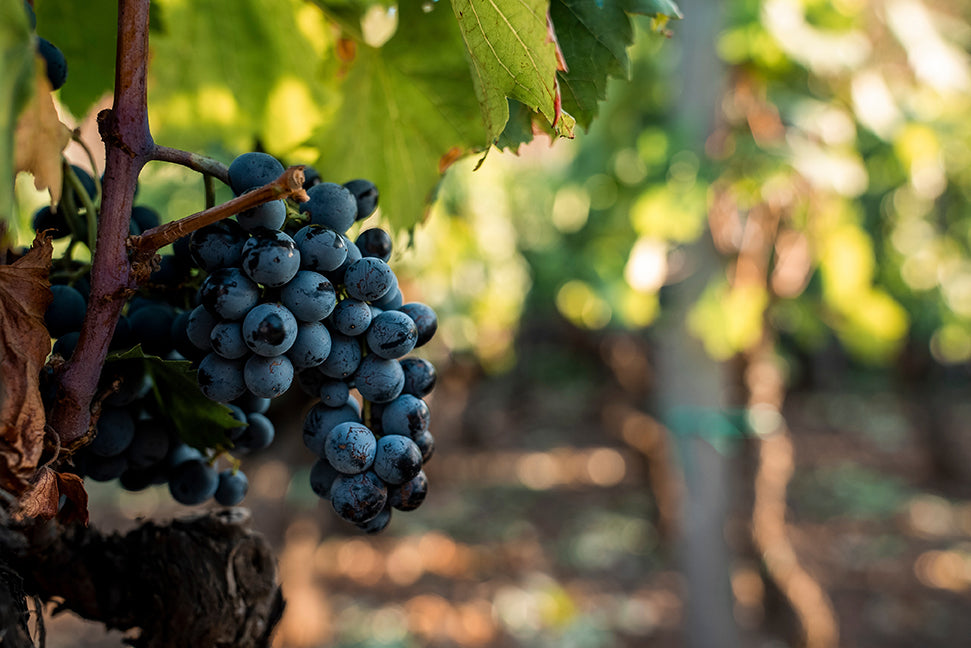
In this episode of the NatureCity Podcast, we explore the cognitive health benefits of potent grapes from the Italian island of Sicily. These gra...
Continue Reading
On this episode of Nature City, we delve into the fascinating topic of CoQ10, which your body needs to produce cellular energy. Your heart, muscl...
Continue Reading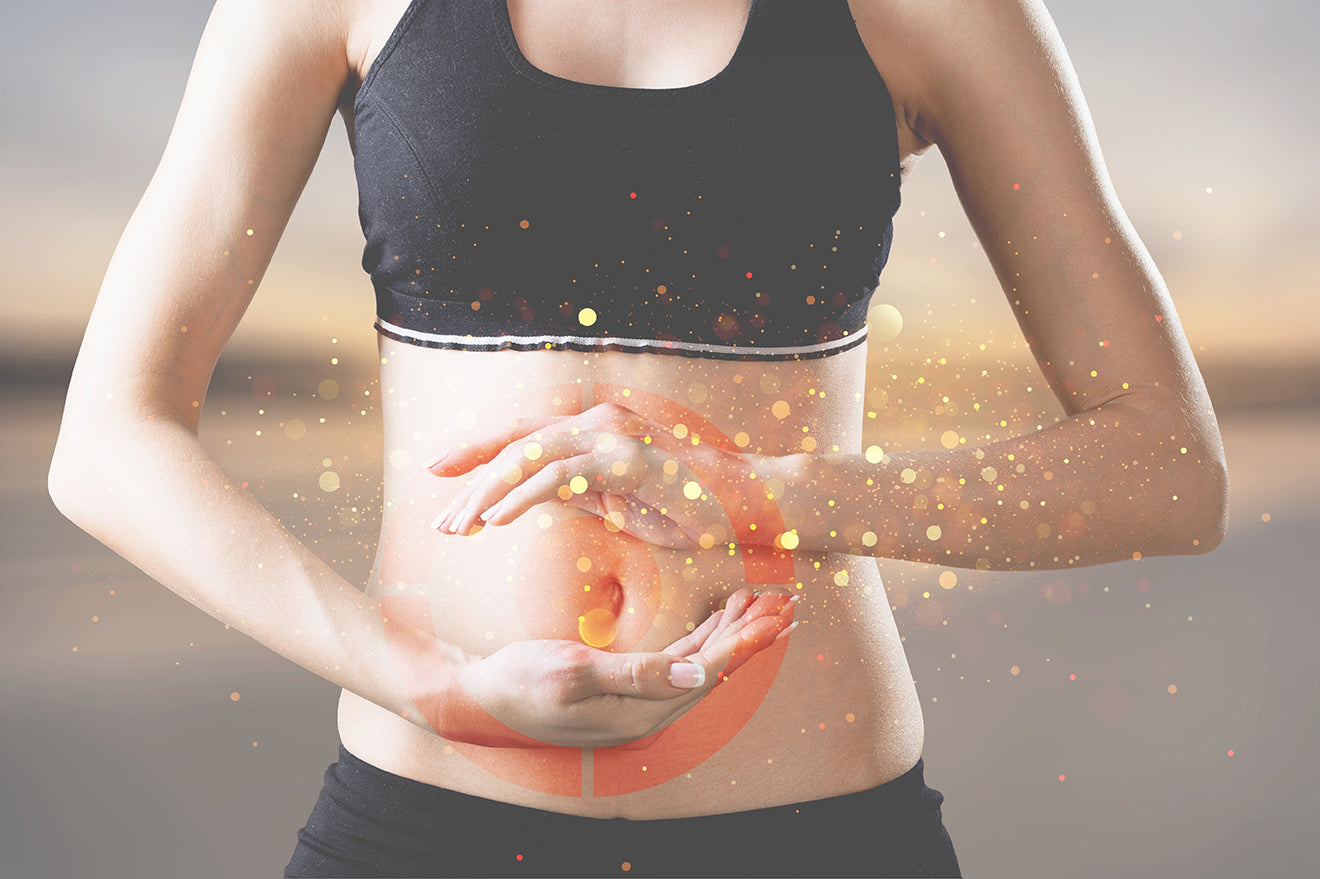
In this episode, Carl introduces True DYB, a revolutionary drink mix that combines 16 ingredients that help you Digest Your Best and supports many ...
Continue Reading
In this episode of the NatureCity Podcast, host Carl Pradelli discusses the remarkable benefits of the pomegranate fruit, and specifically the hi...
Continue Reading
In this episode of the NatureCity Podcast, CEO Carl Pradelli discusses why he believes AMLA is the next herbal superstar nobody's talking about yet...
Continue Reading
Welcome back to another episode of the NatureCity Podcast, your go-to podcast for health and wellness. In this episode, we discuss the importance ...
Continue Reading

In this episode of the NatureCity Podcast, Host Carl Pradelli chats with his good friend and Aloe Vera expert Jeff Barrie. Jeff Barrie has been ...
Continue Reading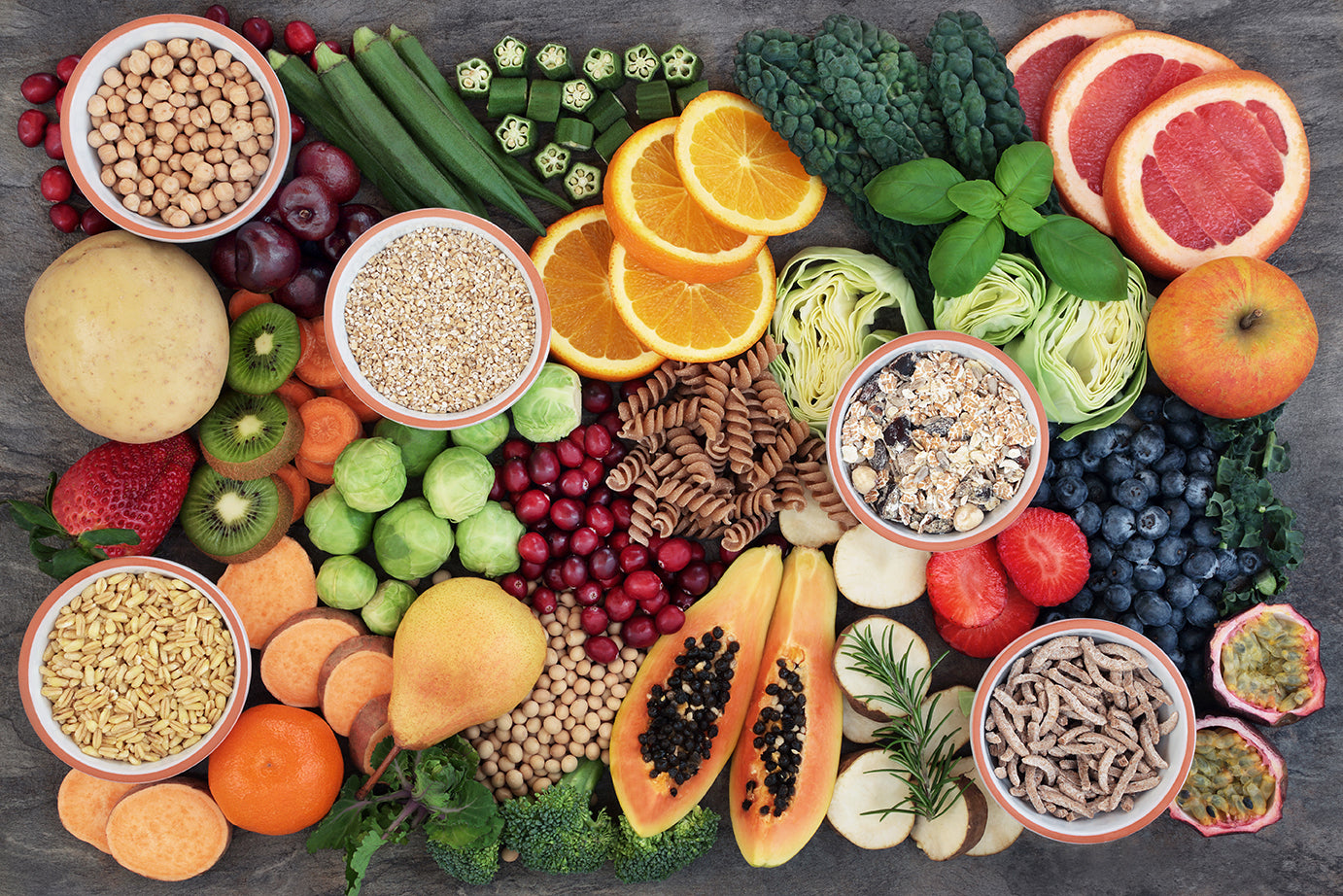
In this episode of Nature City, Carl Pradelli explores the importance of fiber in our diet, the challenges of meeting the recommended daily inta...
Continue Reading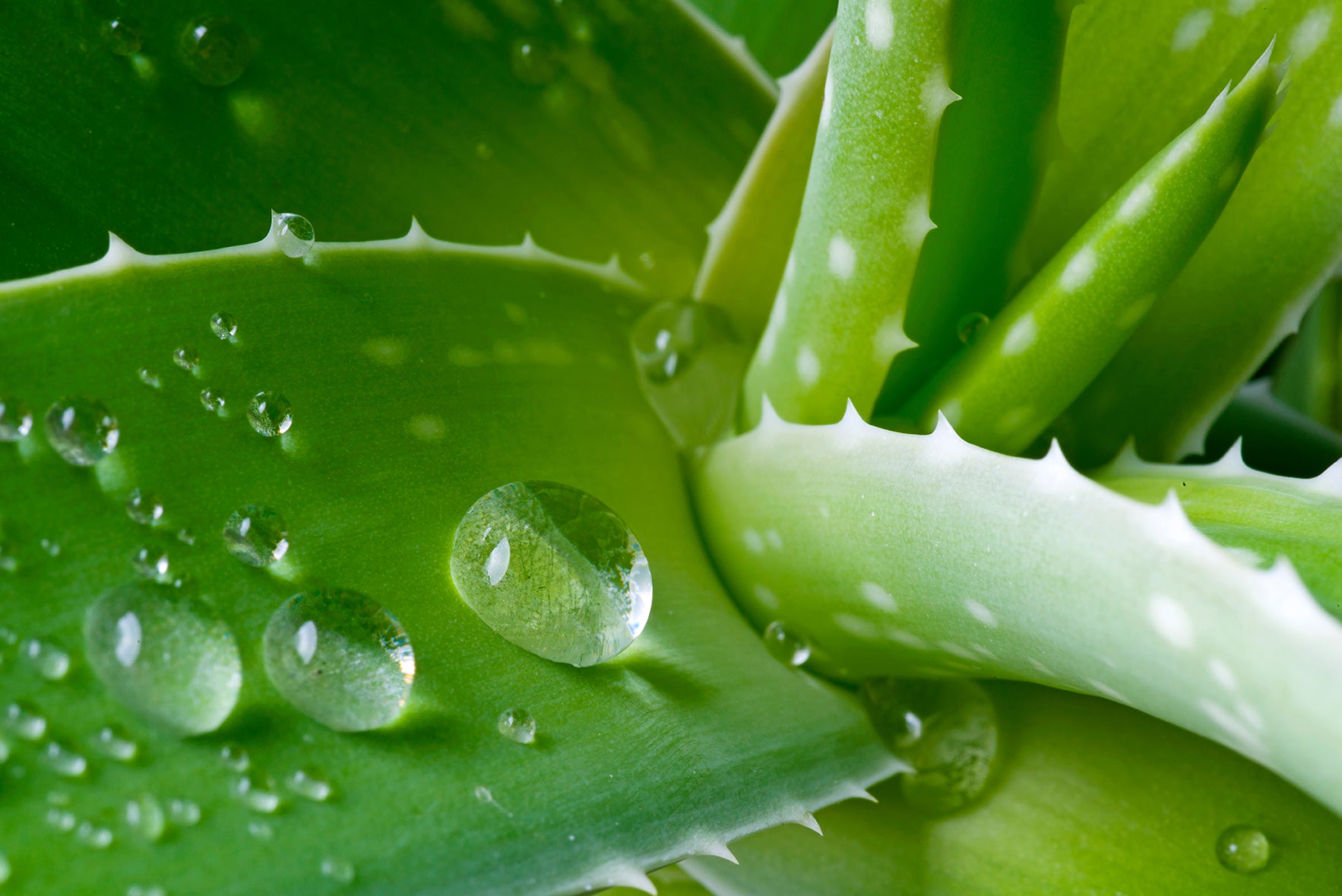
In this episode, we explain how to find a pure and potent Aloe vera supplement. This is important because many products are being made with low qu...
Continue Reading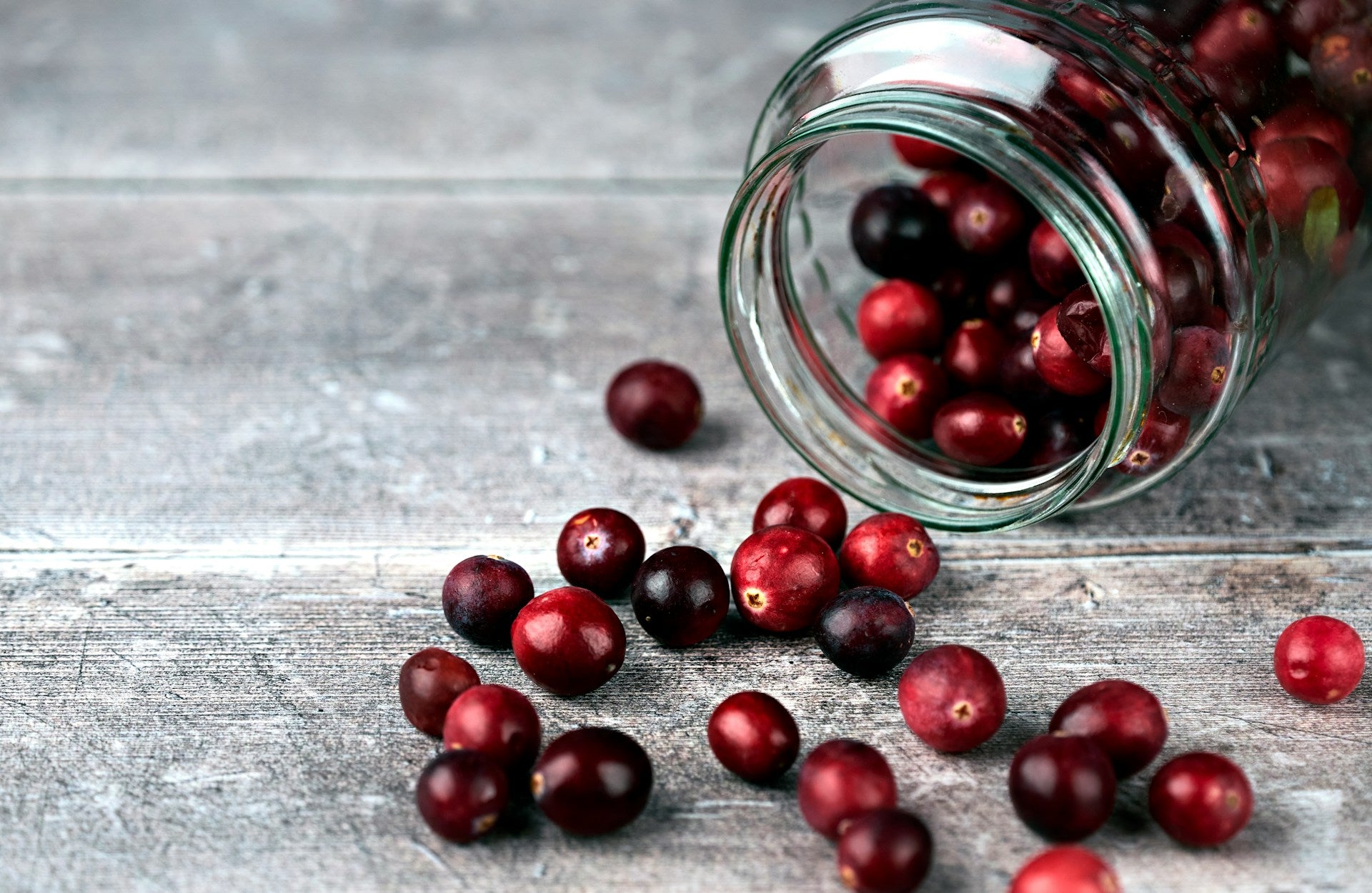
In this episode, Host Carl Pradelli dives deep into the world of cranberries and their incredible health benefits, particularly for urinary tract ...
Continue Reading